Introduction
Embedded operating systems are the unseen force behind many of the smart devices and industrial machines we use today. Unlike general-purpose operating systems, these specialized systems are designed for specific tasks, ensuring high efficiency, real-time processing, and low power consumption. From smartphones and IoT devices to autonomous robots and industrial automation, embedded operating systems shape our digital world.
The embedded OS market is projected to reach $18 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.3%.
What is an Embedded Operating System?
An embedded operating system is a specialized OS designed to run on embedded systems, which are computing devices dedicated to performing a particular function. These systems have limited computing resources and require an OS optimized for efficiency and reliability.
Key Features:
- Real-time processing for critical applications
- Minimal memory footprint for optimized performance
- High reliability for industrial and automation systems
- Power efficiency for battery-operated devices
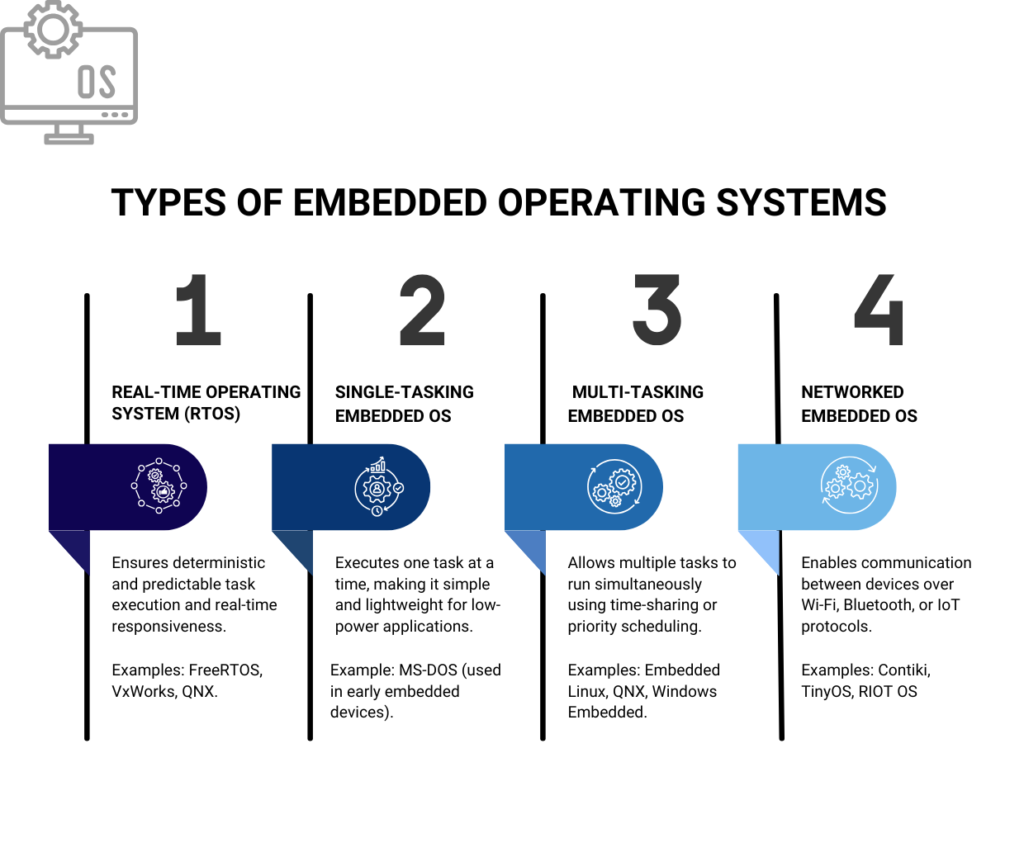
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS)
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is a type of embedded OS that ensures immediate processing and response to inputs. This is crucial in applications such as robotics, automotive systems, and medical devices.
Example: The Robot Operating System (ROS) is widely used in robotics for real-time control and automation.
Network Operating Systems in Embedded Systems
Many embedded devices require network connectivity, and network operating systems facilitate communication between devices. These systems are crucial in IoT ecosystems, allowing seamless data exchange.
Example: The IoT device OS enables smart appliances, industrial sensors, and automation systems to function efficiently.
The Evolution of Embedded Operating Systems
Embedded operating systems have evolved significantly over the years. Early embedded systems had simple firmware with limited functionality. Today, modern operating systems support complex computing tasks with AI integration, automation, and security features.
Key Developments in Embedded OS:
- Embedded Linux OS: A lightweight version of Linux tailored for embedded systems.
- Custom Embedded Linux: Modified versions of Linux designed for specific applications.
- Bare Metal Operating System: Systems running without a conventional OS, directly interacting with hardware.
- AI-Powered OS: Artificial intelligence is enhancing embedded OS efficiency by optimizing performance and predictive maintenance.
Applications of Embedded Operating Systems
Embedded operating systems power a wide range of applications across industries. Let’s explore how they contribute to various sectors:
1. Consumer Electronics and Smart Devices
Devices like smartphones, smart TVs, and IoT gadgets rely on embedded OS for seamless functionality.
- Raspberry Pi Operating System: Popular in education and prototyping projects.
- Android vs iOS Operating System: Both are embedded OS designed for mobile devices.
- Onion Operating System: Used in lightweight web applications and IoT solutions.
2. Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles depend on embedded OS for navigation, safety, and entertainment systems.
- Real-Time Operating System in Cars: Manages engine control, braking, and sensor processing.
- AI-Powered OS in Autonomous Vehicles: Enables self-driving capabilities through machine learning.
3. Robotics and Automation
Industrial robots, robotic arms, and automated machinery require embedded OS for precision and efficiency.
- Robot Operating System (ROS): A leading framework for robotic automation.
- Industrial Automation with Embedded Linux OS: Enhances reliability in manufacturing processes.
4. Healthcare and Medical Devices
Medical equipment such as MRI machines, pacemakers, and monitoring systems operate using embedded OS.
- Embedded Linux in Healthcare: Provides security and stability in medical devices.
- IoT Device OS in Remote Monitoring: Allows real-time patient data tracking.
5. Networking and Telecommunications
Network devices like routers, modems, and cloud servers run on embedded operating systems to handle data processing efficiently.
- Network Operating System: Powers enterprise networking solutions.
- What is the Network Operating System?: Facilitates data transfer in cloud-based applications.
Choosing the Best Operating System for Embedded Systems
When selecting an embedded OS, several factors must be considered:
- Real-time performance: If applications require immediate responses, an RTOS is ideal.
- Security features: IoT and networked devices require advanced security measures.
- Hardware compatibility: Ensuring the OS runs efficiently on selected hardware components.
- Customization: Custom embedded Linux allows fine-tuned performance for specific tasks.
Popular embedded operating systems include:
- Embedded Linux OS: Open-source and widely supported.
- VxWorks: A high-performance RTOS for industrial applications.
- QNX: A secure OS used in automotive and medical industries.
- RTEMS: A real-time OS for aerospace and defense applications.
Future Trends in Embedded Operating Systems
AI-Powered Embedded Systems
Artificial intelligence is transforming embedded operating systems by enabling:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms detect failures before they occur.
- Automated Decision Making: AI-powered OS can adapt and optimize performance in real time.
AI-powered embedded systems improve processing efficiency by up to 40%, reducing energy consumption.
IoT and Cloud Integration
The rise of IoT devices requires embedded OS that support:
- Cloud connectivity: Enables remote monitoring and updates.
- Secure communication: Protects against cyber threats.
Lightweight and Energy-Efficient Designs
Future embedded OS will focus on:
- Minimal resource consumption: Ideal for battery-operated devices.
- Hybrid architectures: Combining bare-metal and traditional OS features.
Conclusion
Embedded operating systems are the backbone of modern technology, enabling smart devices, robotics, and automation to function efficiently. As technology advances, these systems will become even more intelligent, secure, and power-efficient.
“The greatest technology is the one that works so seamlessly, you never notice it’s there.”
FAQs
Q1: What are the three main responsibilities of an operating system?
A: The key responsibilities include process management, memory management, and hardware control.
Q2: How does an embedded operating system differ from a general-purpose OS?
A: Embedded OS is designed for specific tasks, consuming fewer resources, while general-purpose OS handles multiple applications.
Q3: Why is embedded Linux OS widely used in industrial automation?
A: Embedded Linux offers flexibility, security, and real-time capabilities, making it ideal for automation.
Q4: What is the difference between an RTOS and a traditional OS?
A: RTOS provides immediate response times, whereas traditional OS prioritizes multitasking.
Q5: How does AI enhance embedded operating systems?
A: AI-powered OS improves efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time decision-making.
Q6: What role does Devomech play in embedded systems and automation?
A: Devomech specializes in developing innovative embedded solutions for industrial and smart technology applications.

